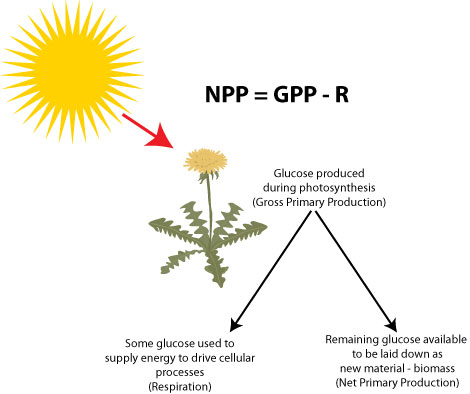
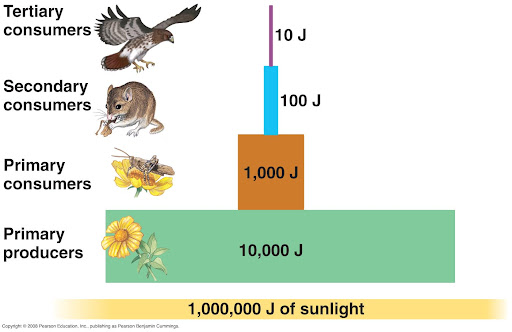
Vocabulary-
CBR- cbr is the amount of people born for every 1,000 people already alive in a population
CDR- Crude death rate is the amount of deaths per 1,000 in a population
TFR- total fertility rate is the average number of people a woman gives birth to over the course of her lifetime
Replacement level fertility-
Replacement fertility is the total fertility rate at which women would have only enough children to replace themselves and their partner.
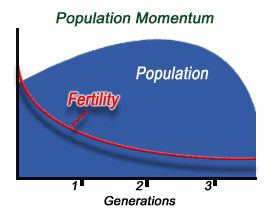
Population Momentum- the growth that occurs even if the replacement level of fertility dropped to anything below 2.1 because the momentum is such that it would continue to grow even if there were less children being born to replace the dead.
Net Migration rate- the number of people that leave and enter the country per 1,000 people
Family Planning- the methods used to help plan for a family such as contraception meds and vasectomies
Affluence- the wealth of the people in a country
IPAT equation- the impact of a countries people on the environment depends on the countries population, affluence, and the technology available
GDP- gross domestic product is the value of everything produced domestically at the end of the year
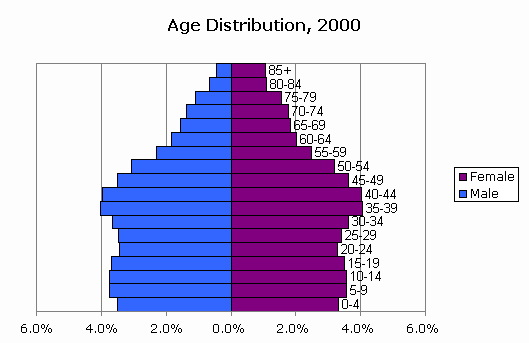
Population pyramid high growth rate-
Stable growth-
Declining growth-
MAKING CONNECTIONS-
The environmental impact is based on a countries affluence, population, and the technology available in that country.
Stage 1- There is only one country in stage one, Lesotho, and it has almost no impact on the environment because it has a small population, very little affluence, and very little technology available to it. It has a very high death and birth rate that prevents it from growing in population terms and the lack of technology keeps them from growing thus keeping them as a farming country in which mainly children are born to help their parents.
Stage 2- As a country transitions to stage two the death rate decreases because of an increase in technology but the country continues to struggle in terms of affluence although the population does grow. Although India, a phase two country, has a relatively high impact on the environment, it is an exception because most phase two countries do not have a high impact.
Stage 3- As a country begins to transition into a phase three country, it starts to impact the environment even more because more technology becomes available to such a large population. The CBR starts to drop because with better family planning and more health care that helps keep the first few children alive hinders the need for more children. Countries such as a the USA and Canada, both phase three, have a large impact on the environment because of the use of factories and technology and cars harms the environment.
Stage 4- A country transitioning to stage four has a lower impact on the environment since its population is less than that of a stage three country, but it still impacts the environment more than a stage 2 or a stage 1 country. More money usually circulates in a stage 4 country and people are more affluent than before. Technology is also very high in a stage 4 country as is health care and family planning.
In this article the journalist reports that because of doctor's not following the guidelines, there have now been 11 women dead and 62 injured in the sterilization process. These deaths are caused by lack of basic hygiene by the doctors and for their use of infected tools on the women during the surgery. The women who decide to undergo sterilization are often paid a laughable amount of 23 dollars or are forced to do so or coerced into being sterilized. One of the doctors, Dr. R K Gupta, performed 83 surgeries in 6 hours! The director of the Reproductive Rights Initiative at the Human Rights Law Network in New Delhi, Kerry McBroom, said that the clinics in which the surgeries are performed are of terrible conditions. India has problems with its population and has to find ways to control it so that they don't reach carrying capacity and can maintain a healthy environment for most people, but as Kerry says, a lot of things can go wrong.
Kerry said:
"You might find that there is no electricity, there is no running water, there is not enough staff in these facilities. They won't have things like blood, in case someone hemorrhages. ... they won't have enough gloves or aprons,".
"Women will go to the facility wearing their clothing and remain in that facility until they go. So there is no attention paid to basic prevention."
With such little health precautions being taken there will obviously be infections and maybe even deaths.
Pro of sterilization- Less children born to help curb the growth of one of the fastest nations in terms of population, the women who participate get payed by the government.
Cons- Poor lack of hygiene can lead to infection or deaths, don't get paid enough to do it, often forced, you can't have anymore children, infringement upon basic human rights.
Big Picture Reflection-
Human Impact- The human population obviously is impacted by humans, but humans impact it in many different ways. In my current event I discuss how human caused overpopulation can lead to making decisions such as government endorsed sterilization. Also humans impact and shape a country and thus decide its fate when it is categorized as a stage 2, 3, or 4 country in the demographic transition model. If the people in the country decide to have 40 children each, an exaggeration but you get the point, then that country will most likely be a stage 2 country because if each mother is having 40 children then that means that the children help the family economically by gaining money working and that out of those 40 children maybe 10 will survive to adulthood because of poor health care and lack of family planning. If countries have too many people then they could reach carrying capacity, this would be cause by humans overpopulating the country in the first place.
Environmental Impact- In the video it says that humans thrive on less than 17% of the earths surface so the impact that we do have on that 17% is massive. In the article the environment actually is the one that impacts us, or in this case the people of India. Because people litter and harm their environment then there is lack of of proper cleaning supplies that then cause the infections that harm the women that get sterilized. Also if there are too many people then that environment might reach carrying capacity and people would be forced to look for different ways to supply their families with food or water. Rivers become murky, shallow water and the land becomes impossible to farm on. The transition between the demographic transition model also shapes the environment in which we live. Brazil was once a country covered with forests and wildlife, now humans have urbanized so much that about 70% of the original Amazon rain forest now remain. The IPAT equation depends on the affluence of the country and their level of technology as well. This can apply to environmental impact or the economic impact.
Economic Impact- The human population depends on the economy. We are at the mercy of the economy. In the 1920s and '30s when the depressions happened a lot of humans lost jobs here in the USA and were forced to make drastic changes to their living situations. People lived on the streets and even migrated to other places in the USA were the depression did not affect them as much. In the country of India the government used and still uses money as an incentive to get a vasectomy or get sterilized. Albeit, the money is around 30 dollars, but still it does impact the government's economy that it has to spend on sterilization when it could be spent creating jobs for the children that could be born. Urbanization and infrastructure because of the growing human population have to resume growing and to be spent on by the people of that country, thus causing taxes to increase and making people mad. By Glade rd it already too overpopulated with cars at peak hours but because the people that live there don't want to pay to expand the road then we are left with 30 minute traffic jambs because of a stop sign or a round-about that people don't know how to go through. The IPAT equation depends on the affluence of the country and their level of technology as well. This can apply to environmental impact or the economic impact.
Government Legislation- There is a lot of government and international legislation even when it comes to the human population. International law mandates that widespread or forced sterilization is a crime against humanity under the
Rome Statute of 1998. This law makes it so that in India the government has to pay you to get sterilized and is not forced but it is highly recommended. In the USA there are no laws to control human population at all and we should be thankful for that.
In countries such as Germany, Japan, Taiwan, Australia and Russia pay people to have children and most of these have declining populations and are stage four countries.